Metal Knowledge Sharing, metal surface pretreatment technology
Release time:2022-02-10Click:1254
Surface pretreatment is the process of mechanical, chemical or electrochemical treatment of materials and their products before surface processing, which makes the surface clean, coarsened or passivated for subsequent surface treatment, also called surface preparation or surface adjustment. Metal surface pretreatment has the following aspects: 1 surface leveling, including mechanical leveling and mechanical polishing, 2 etching, including chemical etching and electrochemical etching, 3 surface oil removal, including organic solvent deoiling, Chemical Deoiling, electrochemical deoiling. Surface leveling mainly includes: Mechanical Polishing, polishing (mechanical polishing, chemical polishing, electrolytic polishing) , rolling, brushing, sandblasting, etc. , according to the surface condition of parts and the specific technical requirements of parts, different surface treatment processes are adopted.
1. The main purpose of mechanical polishing is to make the rough surface of metal parts flat and smooth; secondly, it can also remove the surface of the metal parts burr and oxide scale, rust and sand hole, groove, bubble and so on. Polishing is done with an elastic grinding wheel mounted on a grinder (Fig. 1) . When the grinding wheel rotates at a high speed, the surface of the part to be processed is pressed gently against the grinding wheel working surface, causing the surface of the metal part to be cut on the bulge, and become more flat and smooth. Polishing is suitable for all kinds of metal materials, and its effect mainly depends on the characteristics of Abrasive, the rigidity of grinding wheel and the rotation speed of grinding wheel. The abrasives used for polishing are usually artificial corundum (see Fig. 2, containing 90% ~ 95% alumina) and emery. Artificial corundum is widely used because of its toughness, small Brittleness and many edges and corners of particles.
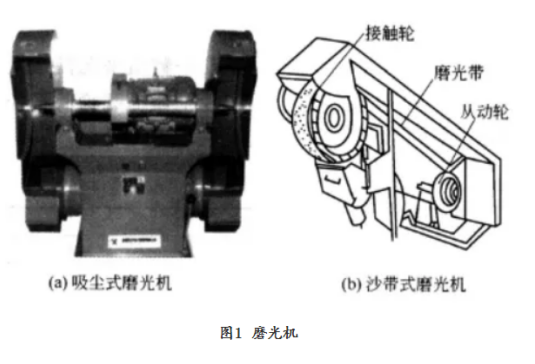
Abrasives can be classified into several grades according to their particle size. Abrasive size is usually divided by the size of the sieve, the sieve number is expressed by the number of holes per unit area (square centimeter) , the larger the size of the sieve, the smaller the holes. The particle size of an Abrasive is indicated by the number by which it passes through the sieve. The larger the number of Abrasives, the finer the particles, the smaller the number, the larger the particles. Table 1 shows the properties and uses of common abrasives. The optimum grinding wheel speed for polishing different metal materials is shown in Table 2.
2 Polishing 2.1 mechanical polishing polishing is a polishing function. The polishing agent “Tears”(grinds) the atoms from the surface layer of the workpiece. The lower layer retains its fluidity for an instant and is smoothed by surface tension before solidifying. It is also considered that polishing is a surface tension effect, in the polishing process, due to friction and heat, can make the surface soften or melt, so it is not simple mechanical polishing. The surface layer of the metal is melted during polishing, but because of the high thermal conductivity of the substrate metal, the surface layer rapidly solidifies into an amorphous state and is smoothed by surface tension and the friction of the polishing agent prior to solidification. For the workpiece with high requirement of fineness, it is polished after fine grinding. Mechanical Polishing is carried out on the polishing wheel of the polishing machine with two kinds of polishing agents: polishing paste and polishing fluid. The former is a mixture of abrasive and adhesive (stearic acid, paraffin, etc.) The latter is a mixture of abrasive and oil or water emulsion. The polishing wheel rotates at high speed, removing the slight unevenness from the workpiece it comes into contact with, giving it a mirror-like Luster. Polishing is used for both pretreatment before plating and finishing after plating to improve Surface finish. The polishing process is different from polishing. Significant metal chips are removed during the polishing process, but not during the polishing process, so the polishing process does not cause significant metal loss. The role of polishing, on the one hand is high-speed rotation of the polishing wheel and workpiece friction caused by the high temperature plastic deformation of the metal surface, thus filling the metal surface of the workpiece, on the other hand, the thin oxide film or other compound film formed immediately by the oxidation of the metal surface in the ambient atmosphere is repeatedly removed, resulting in a smooth and lustrous surface.
2.2 Chemical Polishing (CMP) is a process in which the surface of a metal is flattened and polished by controlling the selective dissolution of the metal through chemical etching in a specific polishing solution under controlled conditions. Compared with other polishing technologies, it has the advantages of simple equipment, low cost, simple operation, high efficiency and no influence of parts shape and structure. Compared with electrolytic polishing, chemical polishing does not need power supply, can deal with more complex shape of the workpiece, high efficiency, but the surface quality is lower than electrolytic polishing. The chemical polishing reaction belongs to the electrochemical process of corrosion micro-battery. Therefore, the principle of chemical polishing is similar to that of electrolytic polishing. In the process of chemical dissolution, a layer of oxide film is formed on the metal surface, therefore, the dissolution rate is faster than the concave part, and the passive oxide film is formed on the surface of the steel parts and the oxide film is dissolved continuously, and the former is stronger than the latter. Because of the inconsistency of the part surface, the part of the micro-bump on the surface is dissolved preferentially, and the dissolution rate is higher than that of the concave part, and the dissolution of the membrane and the formation of the membrane always take place at the same time, as a result, the steel parts are Surface roughness, resulting in a smooth, shiny surface. Chemical Polishing can also effectively remove the surface damage layer caused by mechanical polishing because of its dissolving effect on the surface layer.
2.3 electrolytic polishing is the electrolysis of the workpiece in a specific solution by placing the workpiece on an anode. The current density of the surface of the workpiece is higher and the solution is faster, but the current density is lower and the solution is slower at the microindentation, in order to achieve the flat and light purposes. Electrolytic polishing is often used in the finishing of carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper and other parts, or the finishing of the surface of some tools. Phosphoric acid-chromic Anhydride type polishing solution is widely used in iron and steel materials. The main components are phosphoric acid, sulfuric acid and chromic anhydride, in which corrosion inhibitor, brightener, thickener and other additives are added. In recent years, with the increasing application and output of stainless steel products, the demand of its electrolytic polishing solution is also increasing. In order to prevent environmental pollution caused by the use of electrolytic polishing solution containing phosphoric acid and chromic anhydride, the development of environment-friendly stainless steel electrolytic polishing solution in China has achieved remarkable results. Table 3 lists the solution composition and process conditions of several new stainless steel electrolytic polishing solutions. Formula 1 and 2 in the table do not use chromic anhydride, which solve the problem of waste water discharge and is a new environmental friendly electrochemical polishing agent.
In comparison with mechanical polishing, electrolytic polishing is used to flatten the polished surface by means of electrochemical dissolution, so there is no deformation layer on the surface and there is no foreign material, the polished surface will be formed a layer of oxide film, is conducive to improving its corrosion resistance. In addition, for complex shape parts, wire, thin plate and small parts, mechanical polishing is difficult, can use electrolytic polishing. In addition to leveling effect, electrolytic polishing can also remove surface inclusions, show parts surface cracks, sand hole, inclusion and other defects. 3 barrel finish is often used for surface preparation or surface modification before plating or after plating of large quantities of small parts. It is a kind of processing process that the parts and abrasives are rolled together in the roller or bell-shaped machine to remove the Burr, roughness and rust on the surface of the parts and make the surface smooth. In addition to adding Abrasives, chemical reagents such as acid or alkali are often added in the process of light rolling. Therefore, the essence of light rolling process is the collision and friction between parts and abrasives when they roll together, as well as the action of chemical reagents, but burrs, coarseness, and rust. Fig. 3 is a sketch of a Polisher.

It can remove the oil and oxide scale on the surface of the parts, make the parts have luster. It can replace the polishing and polishing in whole or in part, but it is only suitable for the parts with large quantity and low Surface roughness. There are dry and wet methods of rolling light. Dry Use of sand, emery, broken glass and leather and other abrasives. The wet method uses steel balls, crushed stones, Sawdust, Lye, tea powder, etc. As abrasives. The speed of light rotation depends on the characteristics of the parts and the structure of the drum, usually in 15 ~ 50r/min. If the speed is too high, the parts can not rub with each other because of the Centrifugal Force; if the speed is too low, the efficiency is low. If there is a lot of oil and rust on the surface of the parts when they are rolled, degreasing and etching should be carried out first. When less oil, you can add sodium carbonate, soap, honeysuckle powder and a small amount of alkaline substances or emulsifier together for Rolling Light; parts surface rust can be added dilute sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid. When the parts in the acidic medium after finishing, should immediately wash the acidic liquid clean. 4. Brush polishing is a method of using the brush wheel made of wire, animal hair, natural or synthetic fiber to process the workpiece surface, which is mainly used to remove the oxide scale, rust, welding residue, old paint and other dirt on the workpiece surface; The utility model is also used for removing the burr left on the surface edge after the part is machined. Common brush wheel is generally made of steel wire and brass wire and other materials. Parts of harder materials, should be used rigid steel wire brush wheel, while using a larger speed; conversely, the use of brass wire brush wheel. Brushing can be divided into mechanical brushing and manual brushing. Both are mostly wet, generally using water as a brushing solution, steel materials brush also used 3% ~ 5% (mass fraction) of sodium carbonate or sodium phosphate solution.
5. Sand blasting refers to the use of purified Compressed air, dry sand (such as quartz sand, steel sand, alumina, etc.) is strongly sprayed to the surface of the metal workpiece, grinding the surface of the workpiece Burr, oxide skin, corrosion, carbon deposition, welding slag, molding sand, residual salt, old paint film, dirt and other surface defects. Sand blasting is commonly used to clean the surface of the work piece, such as removing the residual sand and high carbon layer on the surface of the casting, as well as welding seam of the welding piece, removing rust and oxide coating. Descaling generally uses sandblasting and pickling, the latter is easy to make hydrogen permeate into the iron and steel parts, increase internal stress, reduce plasticity, and descaling does not produce hydrogen embrittlement. Whether it is high carbon steel, high strength steel, elastic parts, brass parts, stainless steel parts and aluminum parts after sandblasting into the next process, can improve the coating or oxide adhesion. Hard chrome plating and coating of the workpiece commonly used sandblasting cleaning surface, machine tool accessories and tools before the milky white chrome-coated with sandblasting to extinction. Sand blasting is one of the best surface pretreatment methods. It can not only completely remove the oxide scale, rust, old paint film, oil stain and other impurities on the metal surface, so that the metal surface shows a uniform metallic color, but also can make the metal surface obtain a certain roughness, the surface with uniform roughness can be obtained, and the mechanical stress can be changed into compressive stress to improve the adhesion between the coating and the base metal and the corrosion resistance of the metal itself. In addition to sandblasting, surface roughness treatment methods are car thread method, knurling method, such as electrical discharge roughening. Sand blasting is divided into dry and wet spraying two categories, wet spraying abrasive and water mixed into mortar, in order to prevent metal rust, water to add corrosion inhibitor. Dry spraying has high efficiency, but its surface is rough, dust is big and abrasive is broken. Wet spraying has little pollution to the environment, and it can Polish and protect the surface, so it is often used in precision machining.
6. The purpose of etching is to remove the rust layer, oxide scale (formed during casting, forging, rolling and heat treatment) and other corrosion products. Acid solutions are usually used because they have a strong ability to dissolve metal oxides, hence the term pickling. Some Non-ferrous metal are alkaline pickling. The process of removing large amounts of oxide and poor surface tissue is called strong etching, while the process of removing thin oxide film from the surface of the workpiece before electroplating to obtain an activated surface is called weak etching. Iron and steel pickling acid for inorganic and organic acids, inorganic acids such as sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, phosphoric acid, hydrofluoric acid; organic acids such as acetic acid, fatty acid, citric acid. The effect of organic acid is mild, the residual acid has no serious trouble, it is not easy to rust again, the surface of the work piece is clean after treatment, but the cost of organic acid is high and the rust removal efficiency is low, therefore, it is mainly used for cleaning the rust and dirt inside the power equipment container and other special requirements of the components. INORGANIC ACID has the advantages of high rust removal efficiency, high speed, wide source of raw materials and low price, but the disadvantage is that if the concentration is not controlled properly, the metal will be “Over-corroded”and the residual acid is very corrosive, and the acid solution is not cleaned thoroughly, which will affect the effect of plating. In order to slow down the corrosion of metal and hydrogen embrittlement, the appropriate amount of buffer should be added in the rust remover. Such as Rutin, Hexamethylenetetramine, thiourea, etc. .
Pickling of iron and steel products (1) principle of pickling the role of acid in pickling includes chemical dissolution and mechanical stripping of Oxide on the surface of the workpiece. In sulfuric acid, for example, the acid reacts with Iron Oxides (Feo, Fe3O4) to form iron(2+) sulfate (anhydrous) and ferric sulfate. The reaction of sulfuric acid with Matrix iron through the gap of Oxide scale results in the dissolution of iron and the precipitation of hydrogen. The advantage of the reaction of sulfuric acid with matrix iron is that the new atomic hydrogen can reduce the ferric sulfate with low solubility to the iron(2+) sulfate (anhydrous) with high solubility, thus speeding up the chemical dissolution The hydrogen gas generated under the Oxide scale can produce mechanical cracking and stripping action on the oxide scale, which can improve the pickling efficiency. The disadvantage is that the reaction between sulfuric acid and matrix iron may lead to over-corrosion of the Matrix and change the size of the workpiece.
6. The purpose of etching is to remove the rust layer, oxide scale (formed during casting, forging, rolling and heat treatment) and other corrosion products. Acid solutions are usually used because they have a strong ability to dissolve metal oxides, hence the term pickling. Some Non-ferrous metal are alkaline pickling. The process of removing large amounts of oxide and poor surface tissue is called strong etching, while the process of removing thin oxide film from the surface of the workpiece before electroplating to obtain an activated surface is called weak etching. Iron and steel pickling acid for inorganic and organic acids, inorganic acids such as sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, phosphoric acid, hydrofluoric acid; organic acids such as acetic acid, fatty acid, citric acid. The effect of organic acid is mild, the residual acid has no serious trouble, it is not easy to rust again, the surface of the work piece is clean after treatment, but the cost of organic acid is high and the rust removal efficiency is low, therefore, it is mainly used for cleaning the rust and dirt inside the power equipment container and other special requirements of the components. INORGANIC ACID has the advantages of high rust removal efficiency, high speed, wide source of raw materials and low price, but the disadvantage is that if the concentration is not controlled properly, the metal will be “Over-corroded”and the residual acid is very corrosive, and the acid solution is not cleaned thoroughly, which will affect the effect of plating. In order to slow down the corrosion of metal and hydrogen embrittlement, the appropriate amount of buffer should be added in the rust remover. Such as Rutin, Hexamethylenetetramine, thiourea, etc. .
Pickling of iron and steel products (1) principle of pickling the role of acid in pickling includes chemical dissolution and mechanical stripping of Oxide on the surface of the workpiece. In sulfuric acid, for example, the acid reacts with Iron Oxides (Feo, Fe3O4) to form iron(2+) sulfate (anhydrous) and ferric sulfate. The reaction of sulfuric acid with Matrix iron through the gap of Oxide scale results in the dissolution of iron and the precipitation of hydrogen. The advantage of the reaction of sulfuric acid with matrix iron is that the new atomic hydrogen can reduce the ferric sulfate with low solubility to the iron(2+) sulfate (anhydrous) with high solubility, thus speeding up the chemical dissolution The hydrogen gas generated under the Oxide scale can produce mechanical cracking and stripping action on the oxide scale, which can improve the pickling efficiency. The disadvantage is that the reaction between sulfuric acid and matrix iron may lead to over-corrosion of the Matrix and change the size of the workpiece. The main function of hydrochloric acid is the chemical dissolution of oxides. Hydrochloric acid reacts with Iron Oxides to form iron dichloride and ferric chloride, both of which are highly soluble, so that mechanical stripping is less in hydrochloric acid etching than in sulfuric acid. For loose scale, hydrochloric acid etching speed is fast, matrix corrosion and hydrogen permeation are less, but for tight scale, the consumption of hydrochloric acid pickling alone is large, it is better to use the mixed pickling solution of hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid, play the role of mechanical stripping of hydrogen. Nitric acid is mainly used in the treatment of high alloy steel and is often mixed with hydrochloric acid for Non-ferrous metal treatment. The ability of nitric acid to dissolve iron oxide is very strong, the solubility of ferrous nitrate and ferric nitrate is also very large, and the reaction of hydrogen evolution is small. When nitric acid is used in stainless steel, it will not cause matrix corrosion because of its passivation, but when it is used in carbon steel, the problem of Matrix corrosion must be solved.
Hydrofluoric acid is mainly used to remove Si-containing compounds such as alloying elements in certain stainless and alloy steels, inclusion slag in welds, and residual molding sand on the surface of castings. The mixture of hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid is mostly used to treat stainless steel, but hydrofluoric acid is very corrosive, nitric acid will release toxic nitrogen compounds, also difficult to deal with, so in the application of special attention to prevent the human body.
Phosphoric acid has good solubility in iron oxides and is less corrosive to metals because it can produce a water-insoluble phosphate layer (phosphating film) on the metal surface, which can prevent corrosion and is a good base for painting, generally used for precision parts rust, but high price phosphoric acid. When phosphoric acid is used to remove rust, the main function is to change oxide scale and rust into water-soluble Fe (H2PO4)3 and water-insoluble FEHPO4, FE3(PO4)2. The diffusion of hydrogen is weak. The hydrogen produced in phosphoric acid pickling is 1/10 ~ 1/5 of hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid pickling, and the hydrogen diffusion permeation rate is 1/2 of the latter. For stainless steel and alloy steel, the composition of oxide scale is very complex, often compact structure, in common carbon steel in the rust-removing liquid is difficult to remove, production using mixed acid. ACID pickling of titanium-containing alloy steel with hydrofluoric acid added. The thick and dense oxide scale produced by heat treatment is first “Loosened”in a hot concentrated Alkali solution containing strong oxidant, and then eroded in the mixed acid of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid, or sulfuric acid and nitric acid.
(2) the corrosion inhibitor must be used in the pickling additive pickling solution. It is generally believed that the corrosion inhibitor can form a layer of adsorption film or insoluble protective film on the surface of base metal in the pickling solution. The formation of the film is due to the electrochemical reaction between the metal iron and the acid, which makes the metal surface charged, and the corrosion inhibitor is a polar molecule, which is attracted to the metal surface to form a protective film, thus prevent acid and iron continue to act to achieve corrosion inhibition purposes. From the point of view of electrochemistry, the formed protective film can not only retard the anodic polarization process, but also promote the CATHODIC polarization, restrain the production of hydrogen and slow down the corrosion process. Scale and rust do not adsorb the polar molecules of the inhibitor to form a film, because they react with acid to dissolve the rust through ordinary chemical action and are not charged on the surface. Therefore, the addition of a certain amount of corrosion inhibitor in the rust remover does not affect the efficiency of rust removal. To evaluate the effect of various inhibitors, the most important thing is to determine the inhibition efficiency. The corrosion inhibition efficiency can be obtained by comparing the weight loss [ G/(M2h)] of samples with and without inhibitors in the same medium under the same conditions. The addition amount of different corrosion inhibitors in various acid solution has a certain value. With the increase of the temperature of the pickling solution, the corrosion inhibition efficiency of the inhibitor will also decrease, or even fail completely. Therefore, each inhibitor has a certain allowable temperature.
(3) the type, concentration and temperature of acid used for pickling should be determined according to the material of the work piece, the condition of surface rust layer and oxide scale, and the requirement of surface cleaning quality. Sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid and their mixed acid are commonly used for iron and steel parts. Hydrofluoric acid is added to sulfuric or hydrochloric acid in order to dissolve silicon-containing compounds on the surface of castings. The concentration of sulfuric acid is generally about 20% , under this concentration, the etch speed to the oxide scale is fast and the matrix loss is small. The concentration of hydrochloric acid is usually below 15% because smoke occurs when it is above 20% . With the increase of hydrochloric acid concentration, pickling speed is increased and pickling time is shortened. Table 4 shows the relationship between pickling time and acid concentration in hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid for iron and steel with the same degree of corrosion.
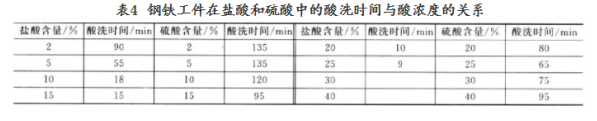
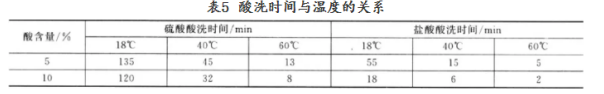
With the increase of temperature, pickling speed is also accelerated and time is shortened. Table 5 shows the relationship between pickling time and temperature in hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid for steel with the same degree of corrosion.
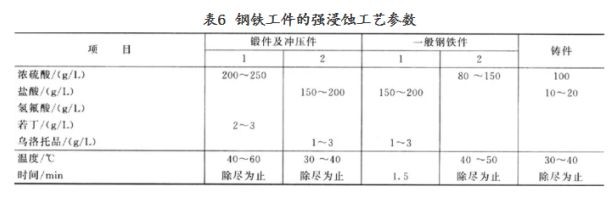
Electrochemical etching electrochemical etching refers to the electrolytic stripping of a work piece as an anode or cathode in an acid or alkali solution, or a method of accelerating the removal of the surface rust layer by agitating the solution due to Cathodic hydrogen evolution and constantly updating the etching solution on the surface of the workpiece. According to the polarity of the workpiece, electrochemical derusting can be divided into two kinds: anodic corrosion and CATHODIC corrosion. During anodic etching, the oxide scale is removed by chemical and electrochemical dissolution of the metal and mechanical stripping of Oxygen. In the CATHODIC etching process, the scale is removed by the mechanical stripping of large amount of hydrogen evolution and the reduction of the oxide by the primary atomic hydrogen. The oxygen bubbles formed during anodic etching are large and small, and the mechanical stripping action is small, and the corrosion of the base metal is easy to be caused by the long time. During Cathodic etching, the metal substrate hardly corrodes and the workpiece size does not change, but hydrogen permeation and ash deposition may occur.
Although anodizing can not cause hydrogen embrittlement, but it is slow and corrosive to the base metal. It is only suitable for thin oxide scale workpiece. The Cathode etching can not cause the workpiece to have over-corrosion, the speed is fast, also can be applied to the thick oxide scale workpiece, but has the shortcoming that causes the workpiece to have the hydrogen permeation. At present, anodic etching or cathodic-anodic combined etching method is widely used in China. Electrochemical etching is used for both strong and weak etching. Compared with the chemical etching method, the electrochemical etching method is easier to remove the oxide scale which is firmly adhered to the metal surface quickly, and even if the acid concentration has some changes, the etching effect will not be significantly affected, and the matrix corrosion is small, and the operation and management are easy, however, this method requires special equipment, to increase hanging with the operation, and oxidation of Uneven scale dissolution phenomenon. The advantages of electrochemical etching are fast etching speed, less acid consumption and the influence of iron ion content in solution on etching ability. But it requires power supplies and energy consumption. Due to the poor dispersion ability, the complicated shape of the workpiece is not easy to be removed. When the oxide scale is thick and dense, chemical strong etching with sulfuric acid should be used first to loosen the oxide scale before electrochemical etching.
Surface degreasing 1. Organic solvent degreasing is a commonly used degreasing method for metal materials. It uses organic solvent to degrease both kinds of oils and fats by physical dissolution. Commonly used degreasing agents include gasoline, kerosene, alcohol, acetone, xylene, trichloroethene, tetrachloromethane and so on. Among them, gasoline and kerosene are cheap, highly solvent and less toxic, it is two kinds of organic solvents with large dosage and common application. Organic solvent oil removal is characterized by no heating, high degreasing speed, no corrosion to metal surface, especially suitable for those with high viscosity, high melting point of mineral oil which is difficult to remove with Lye, therefore, it is suitable for the pretreatment of almost all surface treatment technologies, especially the initial degreasing of parts with serious oil pollution or metal parts easily corroded by alkaline degreasing liquid. But this kind of degreasing is not complete, need to use chemical method and electrochemical method to add degreasing again, and most organic solvent is flammable, poisonous, cost is higher, so operation should pay attention to safety, strengthen protection, keep good ventilation.
2. Chemical Deoiling in alkaline solution the chemical deoiling in alkaline solution is widely used in production at present. Although the oil removal time of this method is longer than that of organic solution, but the medium is non-toxic, does not burn, the required equipment is simple, easy to operate, the price is cheap, so this method of oil removal is reasonable. The essence of this method is to remove oil by SAPONIFICATION and EMULSIFICATION, the former can remove animal and vegetable oils, the latter can remove mineral oils. As long as the proper process selection, the removal of the two types of grease is not difficult. However, when the adhesion of the coating is required to be high, it is not enough for the coated parts to be chemically degreased only in an alkaline solution, especially when the oil stain is mainly mineral oil, not only the degreasing time is long, but also it is not easy to be completely removed, this is because the emulsification of alkaline deoiling solution is limited, so it is necessary to use electrochemical (electrolytic) deoiling with stronger emulsification in order to obtain satisfactory results.
3. Electrochemical deoiling the metal parts to be deoiled in the deoiling liquid, the parts as anodes or cathodes, and through DC electric deoiling method, known as electrochemical deoiling or electrolytic deoiling. The composition of the electrochemical deoiling solution is similar to that of the chemical deoiling solution. Usually with a nickel plate or nickel-plated iron plate as the opposite electrode, it only plays a conductive role. The production practice has proved that the speed of electrochemical deoiling is several times higher than that of Chemical Deoiling, and the oil pollution is clean, which is inseparable from the mechanism of electrochemical deoiling. New Technology of surface pretreatment 1. The ultrasonic wave strengthens the High Frequency Oscillation Signal which sends out by the ultrasonic power source, transforms into the High Frequency Mechanical Oscillation through the transducer, and using the principle that ultrasonic wave can effectively spread in the medium of gas, liquid, solid, solid solution and so on, and can transfer very strong energy, through the cleaning tank wall to the cleaning liquid in the tank to radiate ultrasonic wave, the micro-bubble in the liquid in the tank vibrates under the action of sound waves, that is, reflection, interference, superimposition and resonance will occur through ultrasonic waves and when ultrasonic waves propagate in the liquid medium, it can produce strong impact and cavitation on the interface. The effect of ultrasonic cleaning depends on the type of cleaning solution, cleaning method, cleaning temperature and time, ultrasonic frequency, power density, number and complexity of cleaning parts. Ultrasonic cleaning liquid with organic solvents, Lye, aqueous cleaning liquid and so on. The most commonly used ultrasonic cleaning degreasing device consists of a Ultrasonic transducer, a cleaning tank and a generator, in addition to cleaning liquid circulation, filtration, heating and transportation devices. Ultrasonic cleaning is a new cleaning method, simple operation, cleaning speed, good quality, so it is widely used.
2. Low temperature and high efficiency oil remover high efficiency oil remover low temperature and high efficiency oil remover oil remover to metal surface oil, not only high oil removal efficiency, but also oil removal temperature, to save energy. 3. Vacuum degreasing cleaning vacuum degreasing cleaning is a new cleaning technology with less pollution. The cleaning agent used is a hydrocarbon-based cleaning agent, which has little effect on human body, low stimulation and odorless. The cleaning effect achieves the same cleaning degree as triethanolamine, which is better than Lye, and the cleaning agent can be recycled and regenerated. Vacuum degreasing cleaning device is pollution-free, is a closed system, and high Factor of safety, high productivity, automatic loading and unloading of materials, easy to operate. Vacuum degreasing technology, whether it is no cleaning or liquid cleaning, its future applications will be more extensive. 4. In order to detect the fatigue crack and the hard damage of the coating layer on the surface of the important large-scale components such as aircraft, the coating layer must be removed first. The traditional methods are chemical stripping or grinding by grinding wheel, but both of them have disadvantages, such as chemical stripping has corrosion and damage to metal substrate, grinding wheel is easy to damage substrate, and the efficiency of removing coating is very low. Recently, a new technology of removing paint by spraying plastic pellets has been developed, and the effect is good. The depainting of plastic shot is that the granular plastic is sprayed to the surface of the work piece at high speed by a spray gun under the action of the Compressed air, and the paint layer is split and peeled off under the action of the sharp edge cutting and impact hitting of the plastic shot, in order to achieve the purpose of high-efficient paint removal.
2. Low temperature and high efficiency oil remover high efficiency oil remover low temperature and high efficiency oil remover oil remover to metal surface oil, not only high oil removal efficiency, but also oil removal temperature, to save energy. 3. Vacuum degreasing cleaning vacuum degreasing cleaning is a new cleaning technology with less pollution. The cleaning agent used is a hydrocarbon-based cleaning agent, which has little effect on human body, low stimulation and odorless. The cleaning effect achieves the same cleaning degree as triethanolamine, which is better than Lye, and the cleaning agent can be recycled and regenerated. Vacuum degreasing cleaning device is pollution-free, is a closed system, and high Factor of safety, high productivity, automatic loading and unloading of materials, easy to operate. Vacuum degreasing technology, whether it is no cleaning or liquid cleaning, its future applications will be more extensive. 4. In order to detect the fatigue crack and the hard damage of the coating layer on the surface of the important large-scale components such as aircraft, the coating layer must be removed first. The traditional methods are chemical stripping or grinding by grinding wheel, but both of them have disadvantages, such as chemical stripping has corrosion and damage to metal substrate, grinding wheel is easy to damage substrate, and the efficiency of removing coating is very low. Recently, a new technology of removing paint by spraying plastic pellets has been developed, and the effect is good. The depainting of plastic shot is that the granular plastic is sprayed to the surface of the work piece at high speed by a spray gun under the action of the Compressed air, and the paint layer is split and peeled off under the action of the sharp edge cutting and impact hitting of the plastic shot, in order to achieve the purpose of high-efficient paint removal.
Source: Caitong
Disclaimer: Some pictures and texts on this site are collected from the Internet and are only for learning and communication. The copyright belongs to the original author and does not represent the views of our site. This site will not bear any legal responsibility. If your rights are violated, please contact us to delete it in time.


