The production process and processing methods of copper pipes
Release time:2024-09-18Click:525
What is copper pipe
The so-called copper pipe refers to a seamless pipe made of copper that has been pressed and drawn. Copper pipes are loved by people for their lightweight, good thermal conductivity, durability, and corrosion resistance. Copper pipes are widely used and have the largest quantity in the electrical and electronic industries. Copper pipes can be divided into shaped pipes and round pipes according to their shape. And shaped tubes can be divided into elliptical tubes, square tubes, rectangular tubes, triangular tubes, hexagonal tubes, drip shaped tubes, pentagonal tubes, outer and inner circular tubes, spiral tubes, inner ribbed tubes, outer ribbed tubes, plum blossom tubes, and so on. Copper pipes are divided into extruded pipes, drawn pipes, welded pipes, flexible pipes, and semi-rigid pipes according to production methods and performance. Copper pipes can be classified into copper pipes, brass pipes, bronze pipes, and white copper pipes according to their alloy composition. Finally, it can also be divided into condenser tubes, air conditioning tubes, heat dissipation tubes, waveguide tubes, oxygen generator tubes, aerospace tubes, antenna tubes, etc. according to their purposes.
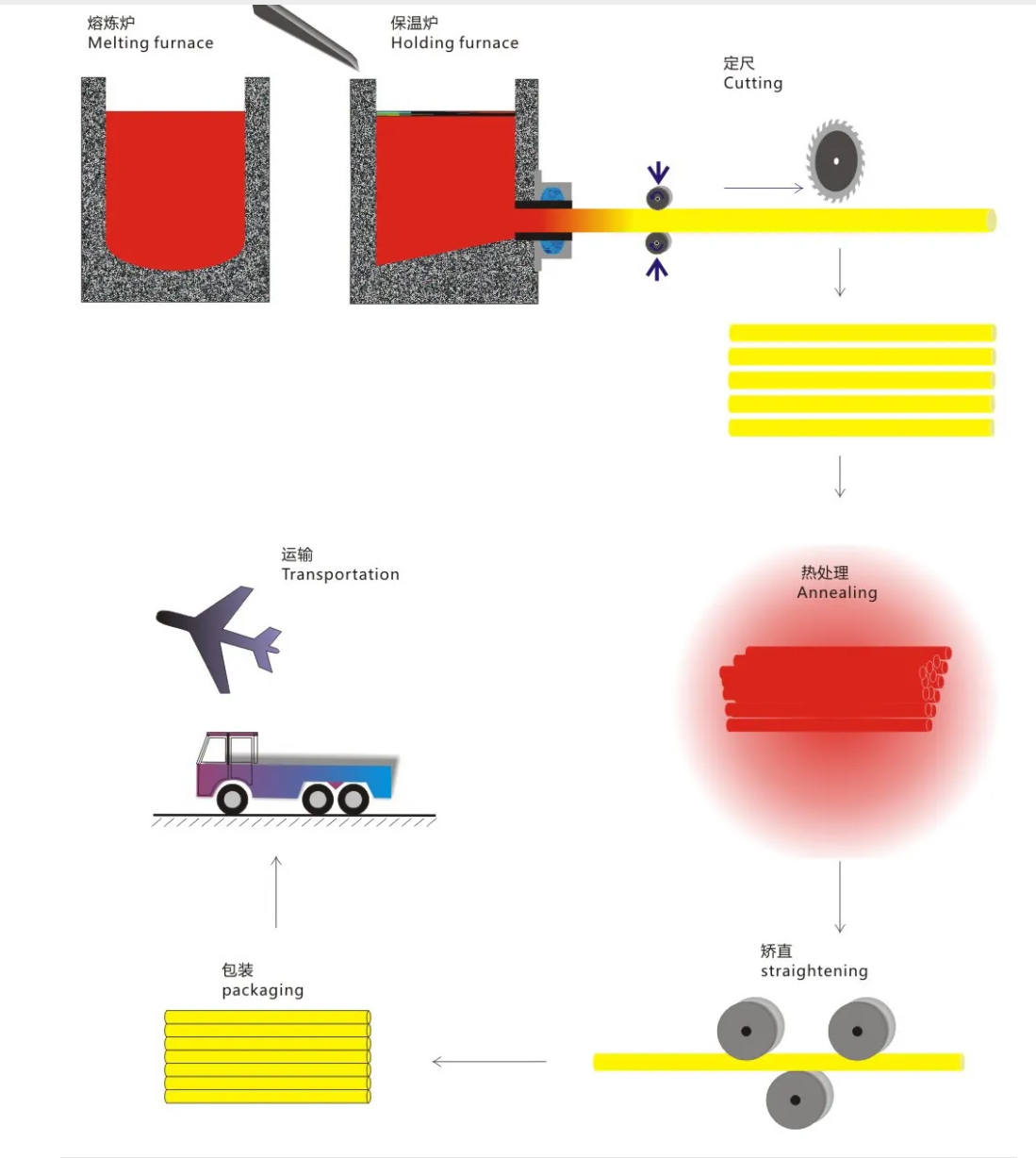 Squeezing and Pulling
Squeezing and Pulling
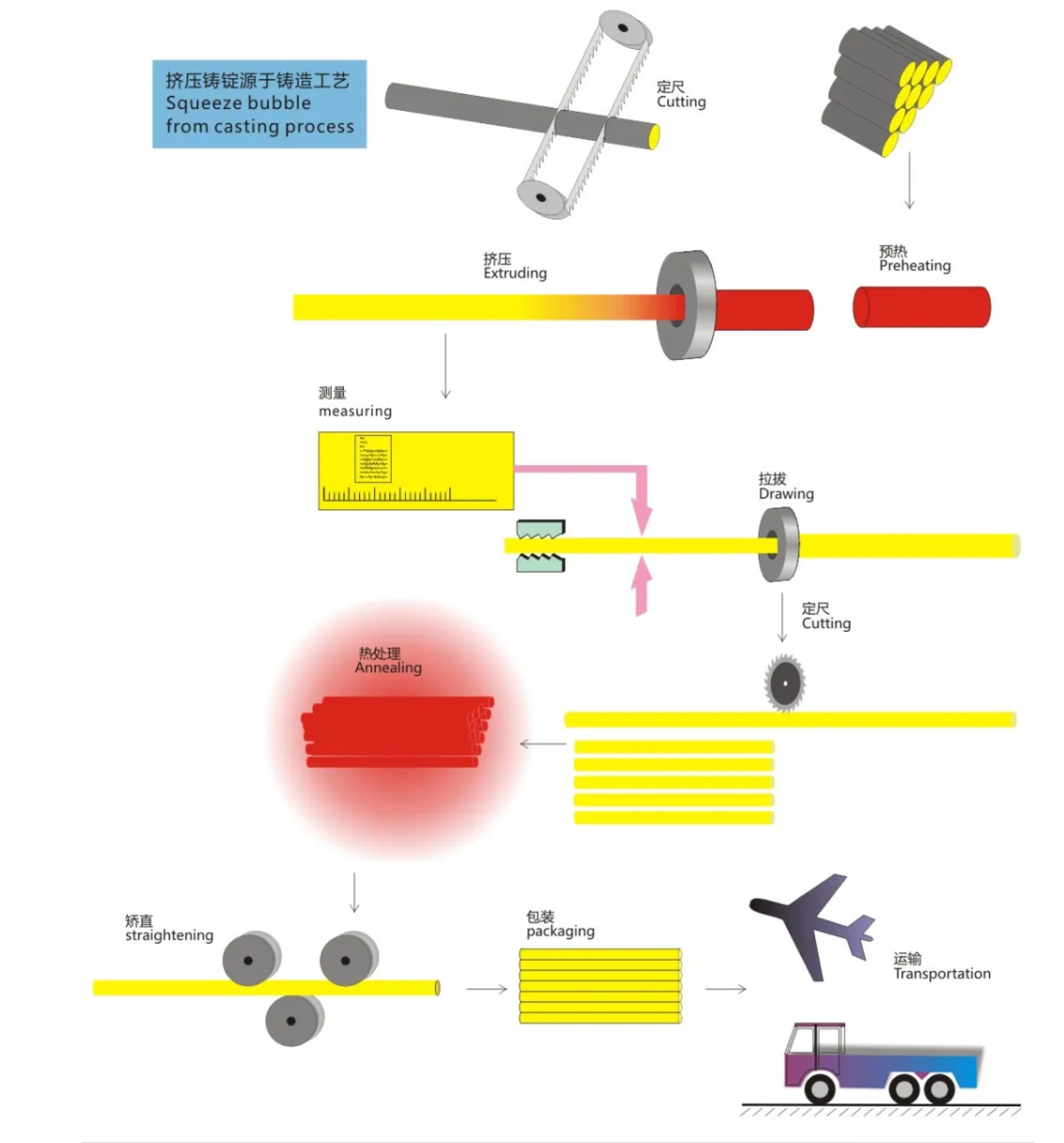
The technical requirements for copper tube processing are as follows:
1. The processing of pipelines should be carried out according to the design drawings, and the shape and size should meet the design requirements.
2. The diameter change at the fracture should be within 2% of the standard diameter of the copper pipe, and there should be no burrs or burrs on the fracture.
3. The pipe fittings should be degreased, cleaned, and free of copper shavings. The inner and outer surfaces should be smooth and free of oil stains, scars, and oxide scales.
4. The welding process must be protected with nitrogen, and the interior should be blown clean with dry compressed air at 2.8-3.0MPa after welding.
The methods for processing copper pipes are as follows:
1. Precision cutting and processing of various precision small tubes.
2. Grinding and sharpening of various precision small tube cutting end faces.
3. Processing of various precision small tube expansion and closure.
4. For various precision small tube bending and forming processes.
5. Processing the side profile of various precision small tubes.
6. Welding, assembly, polishing and processing of various precision small tubes.
7. Perform graded compression and expansion processing on various precision small tubes.
8. Multi station stretching and forming of various tubular products.
9. For porous wall hollow products of pipe fittings.
There are three methods for processing copper pipes:
1. Explanation of copper tube extrusion process: The definition of extrusion process is that the copper billet tube is extruded and formed by a copper tube extruder, so as to make the density distribution of the copper tube more uniform, and the wall thickness is also evenly distributed, thereby achieving stronger compressive strength performance.
2. Explanation of Copper Tube Continuous Casting and Rolling Process: The definition of continuous casting and rolling process is continuous casting and rolling, in which liquid copper burned at high temperature is poured into the continuous casting machine to roll out copper billets (called continuous casting billets), and then directly enters the hot rolling mill without cooling, after being kept in the soaking furnace for a certain period of time. The continuous casting and rolling process cleverly combines the casting and rolling processes, and compared with the traditional process of casting copper billets first, heating them in a heating furnace, and then rolling them, it has the advantages of simplifying the process, reducing labor, increasing metal yield, saving materials, enhancing the quality of continuous casting billets, and producing energy-saving and environmentally friendly copper products. It directly realizes the advantages of mechanization, programming, and automation in one step.
3. Explanation of Copper Tube Upward Drawing Process: The original feature of upward drawing continuous casting copper tubes is "oxygen free", which means that the oxygen content is below 10ppm. Electrolytic copper is melted into copper liquid at high temperature, converted, and hardened into shape. Throughout the entire process, techniques such as charcoal reduction, flake graphite covering, and oxygen isolation are used. Oxygen exists in the form of copper oxide and cuprous oxide in molten copper liquid. Charcoal can deoxidize itself under high temperature, making its oxygen content less than 10ppm. The CO protective gas generated during the chemical reaction process and the oxygen barrier effect of flake graphite prevent graphite from being oxidized during the crystallization process, thus achieving the effect of the upwelling process.
Equipment and operational requirements for cutting and deburring copper pipes:
1. Tools used: pipe cutter, effective ruler, positioning block. Measure the corresponding length with a ruler according to the size and diameter required by the drawing, and place the positioning block.
2. After the copper pipe needs to be positioned and fixed, it should be removed with a cutting knife to ensure that the cutting edge is flat and not deformed.
3. During operation, gloves are not allowed, but deburring can be done with gloves to prevent yarn from entering the copper pipe.
4. During the cutting process, the copper tube is fed evenly to ensure a smooth pipe opening.
5. When the diameter of the pipe is less than or equal to Φ 12mm, multiple (no more than 10) pipes can be cut together; Copper pipes with a diameter greater than Φ 12mm or a length less than 60mm must be cut separately.
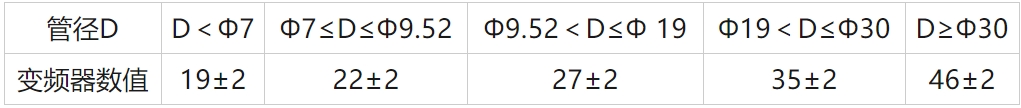
6. After cutting, the port must be deburred using a wire grinder. The size of the frequency converter should be adjusted according to different pipe diameters to cont
 7. After deburring, it is necessary to use dry compressed air at 2.8-3.0MPa to blow away copper shavings and debris inside and outside the pipe.
7. After deburring, it is necessary to use dry compressed air at 2.8-3.0MPa to blow away copper shavings and debris inside and outside the pipe.
Article source: Internet


